How to Deploy Scheduled Tasks with Intune
We’re all sick of scheduled tasks, but let’s face it; you probably still need to deploy them on your Windows machines. And now that you’re invested in the brave, new world of Intune, you’re going to need a way to deploy them.
This guide will serve as a written companion to my recent video, “How to Deploy a Scheduled Task with Intune”. You can watch it here.
What Are Scheduled Tasks?
Scheduled tasks execute commands triggered by a specific event, whether it’s running a PowerShell script or performing system checks. When configured correctly, they save you time, effort, and frustration, leaving you free to focus on the bigger picture.
You have two options for deploying tasks through Intune.
Method 1: The PowerShell and Packaging Way
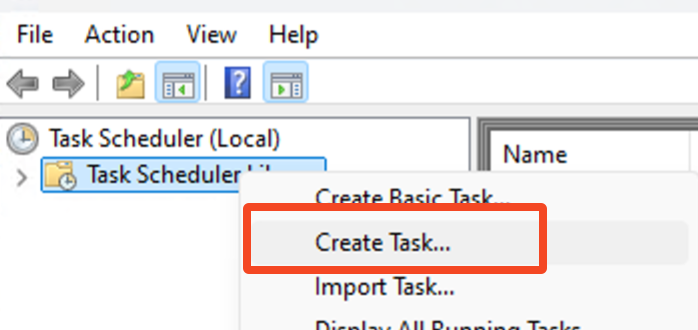
Step 1: Use Task Scheduler to Build the Blueprint
Launch Task Scheduler and create a new task.
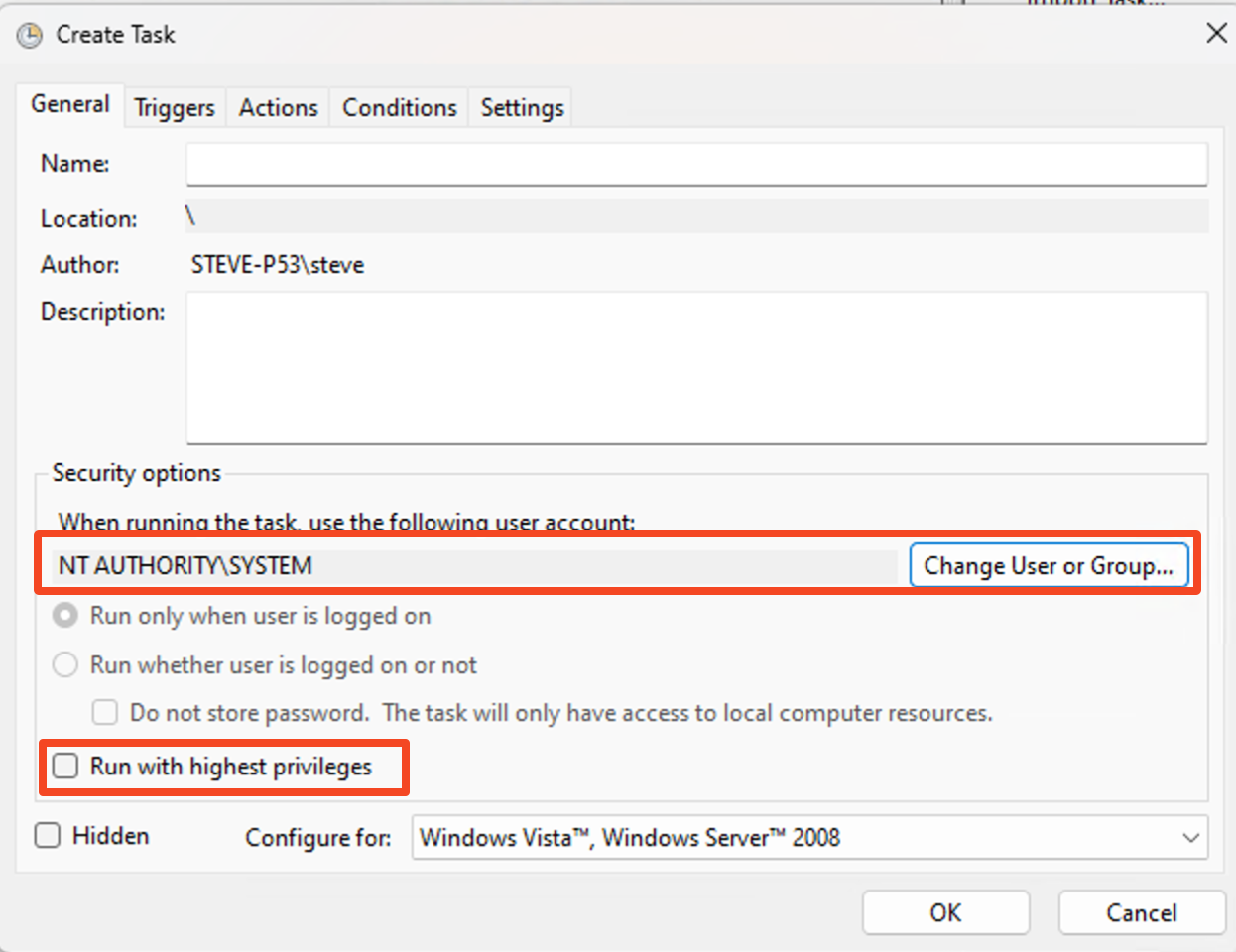
Fill in the details:
Name: Something descriptive, like “Primary User Check.”
Security: Set it to System with the highest privileges. Your task deserves to run with authority.
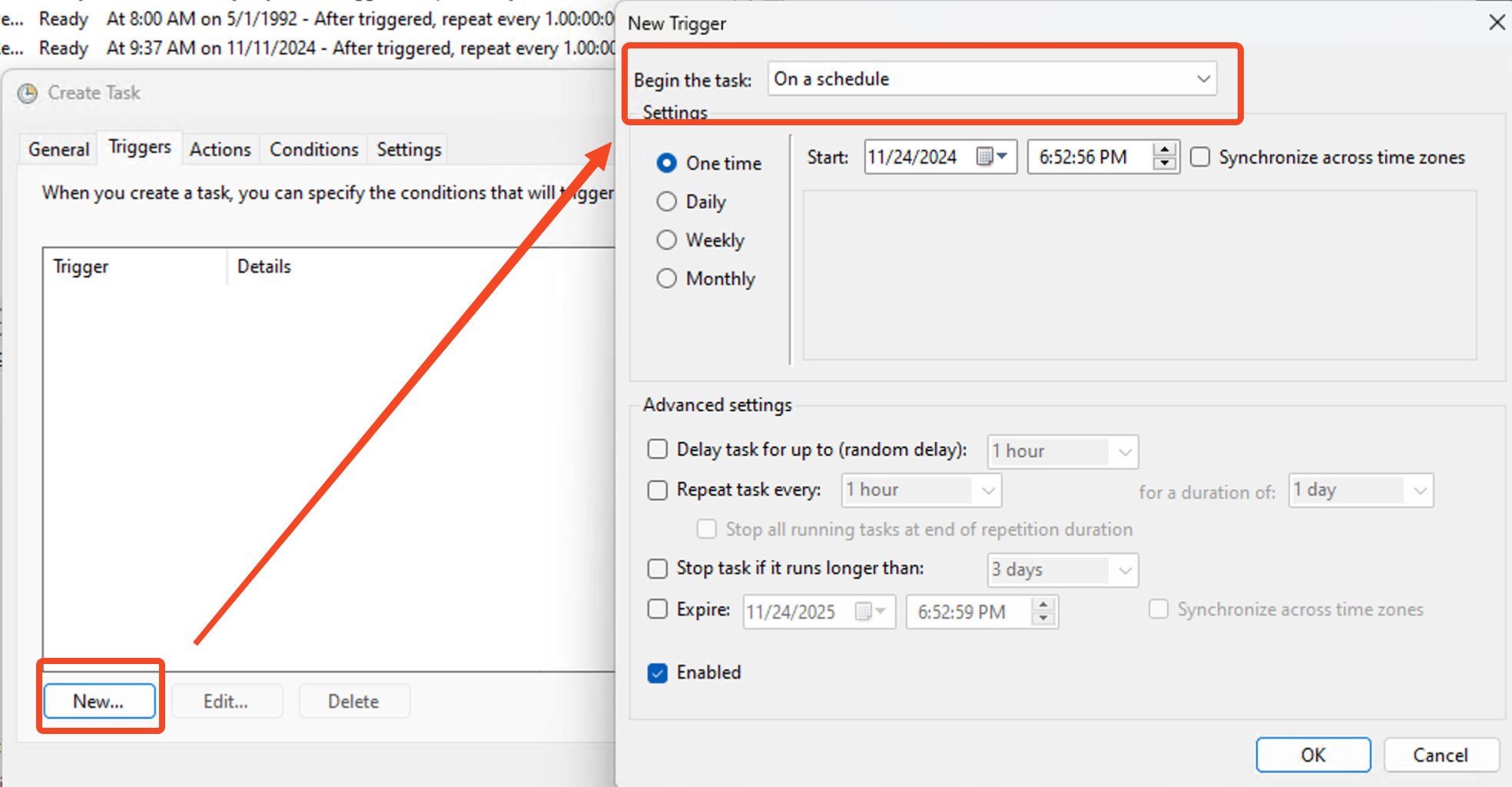
Set Triggers:
Example: Run at logon, with a one-minute delay for better performance.
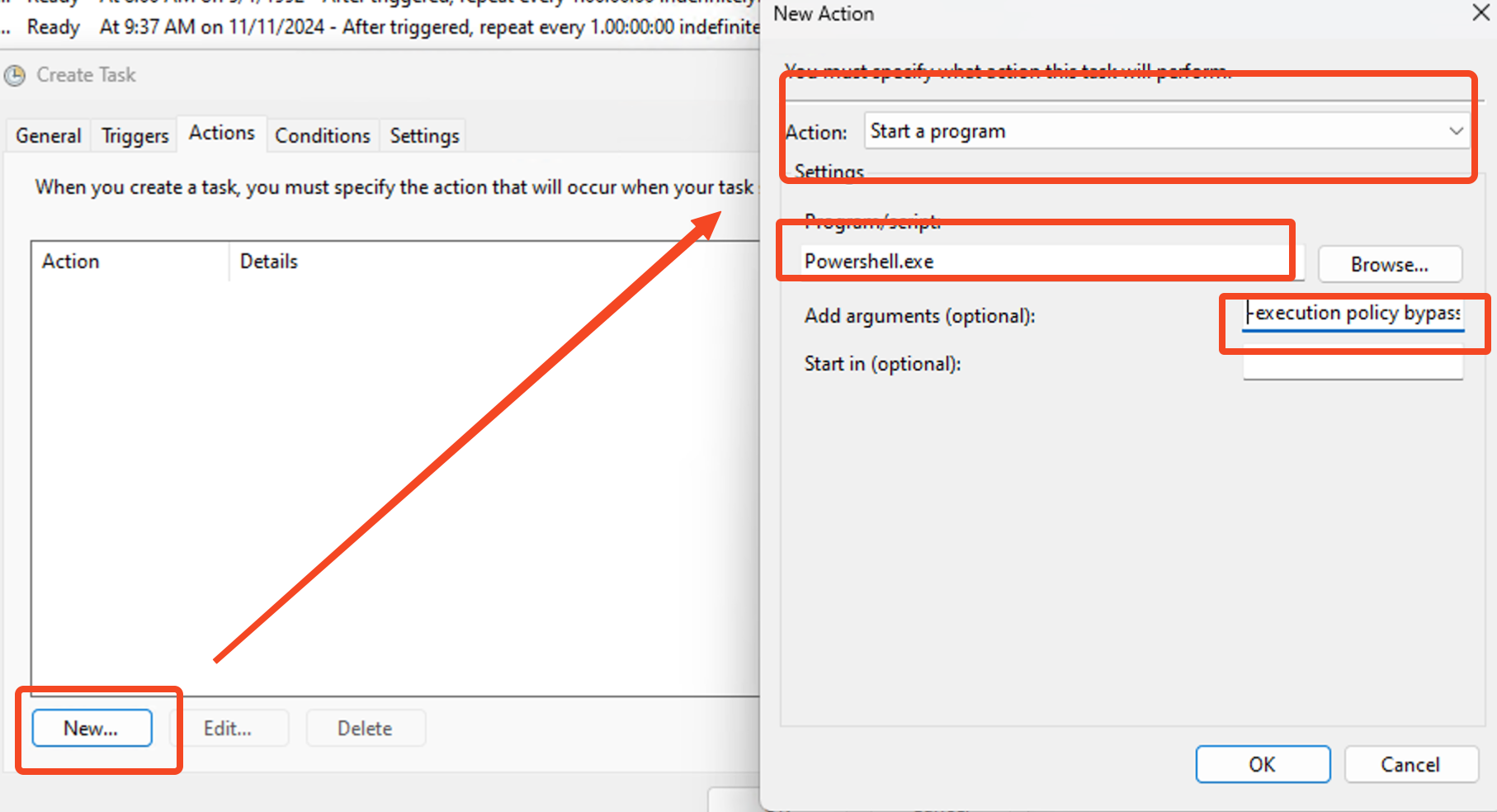
Configure Actions:
Start a program, such as PowerShell, and include arguments like
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File C:\Scripts\UserCheck.ps1.
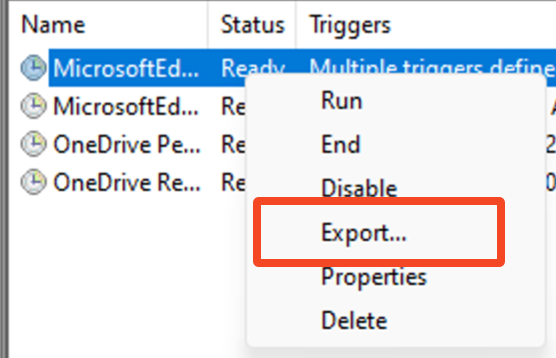
Step 2: Export the Task
Save the task configuration as an XML file. This will serve as your deployment template.
Step 3: Package Your Task and Scripts
Gather your XML file and any required PowerShell scripts.
PowerShell script to deploy task XML found in the GitHub link here.
Use the Intune Content Prep Tool to bundle them into a Win32 app.
Step 4: Deploy via Intune
Upload your packaged app into Intune, configure detection rules, and assign it to the appropriate devices or users.
Method 2: Direct PowerShell Deployment (Quick and Effective)
For simpler needs or when you’re short on time, deploy the task directly via a PowerShell script.
Step 1: Write the PowerShell Script
Create a script that handles everything from task creation to execution. Here’s an example:
$TaskAction = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "PowerShell.exe" -Argument "-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File C:\Scripts\UserCheck.ps1"
$TaskTrigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtLogon
$TaskPrincipal = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal -UserId "SYSTEM" -LogonType ServiceAccount -RunLevel Highest
Register-ScheduledTask -Action $TaskAction -Trigger $TaskTrigger -Principal $TaskPrincipal -TaskName "Primary User Check"
Step 2: Deploy Through Intune
Go to Devices > Scripts in Intune and upload your script.
Ensure you enable the option to run in 64-bit PowerShell. That part matters.
Pro Tips for Tasks
Choose the Right Method: Use the packaging method for larger, more complex tasks. Stick with direct scripting for quick setups.
Stay Organized: Keep scripts and configurations in a central location, like
C:\ProgramData\Scripts, for easy management.Test Before Deploying: Always verify your task on a reference machine before rolling it out across the network.
Why This Matters
At this time, deploying scheduled tasks with Intune is essentially required for medium to large size organizations, especially during the transition to cloud-native Windows management. Once you get the hang of it, they’re actually one of the easier things to deal with in the Intune world.
Good luck!